Mohs Micrographic Surgery
Electrodesiccation and Curettage
Skin Cancer Excision Surgery
Radiation Treatment for Skin Cancer
Radiation therapy may occasionally be recommended instead of surgery if the skin cancer is located in a hard-to-treat place, is particularly large, or if the patient is unable to undergo surgical treatment. Radiation therapy is performed at a radiation center usually in multiple sessions by a radiation oncologist, a doctor who specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat cancer.
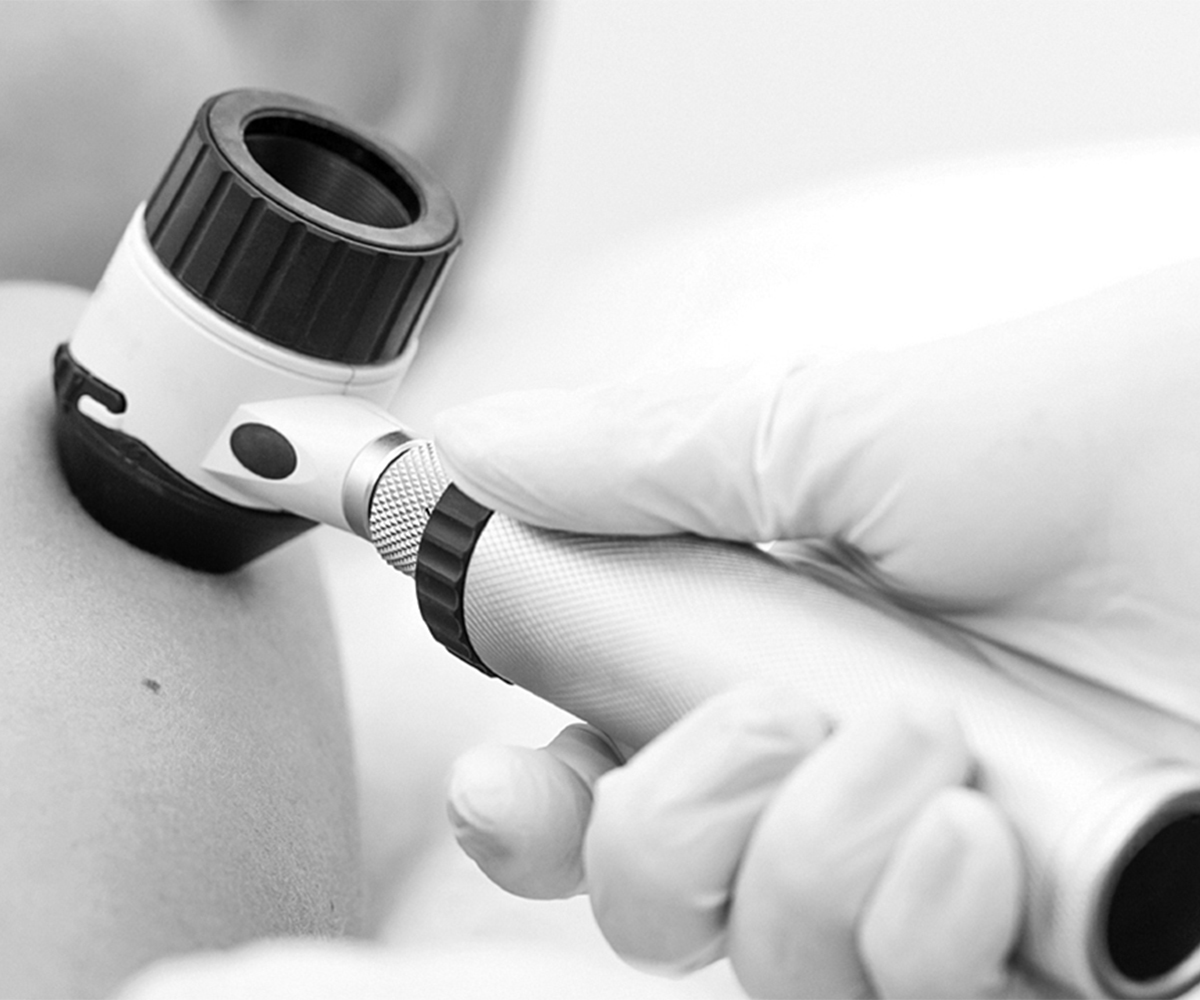
Skin Biopsy
For a shave biopsy, a razor or scalpel is used to take the tissue sample. The depth of the incision varies depending on the type of biopsy and the part of the body being biopsied. An adhesive bandage is then placed over the site to protect the wound.
Cryotherapy
Intralesional Injection
Intralesional injections are an effective way of delivering medication directly into a specific area to treat skin conditions. It can improve the appearance or reduce symptoms of skin lesions and conditions such as scars, keloids, cysts, acne, and alopecia.










